Beyond the Monolith: A Structured Approach to Database Modernization on AWS
News | 04.02.2026
Introduction
For many enterprises, monolithic databases have been the backbone of business-critical applications for years. However, as organizations migrate to Amazon Web Services and adopt cloud-native and microservices architectures, these databases increasingly become a limiting factor. Tight coupling, rigid schemas, scaling constraints, and high licensing costs slow innovation and prevent independent deployment of services.
In practice, many organizations successfully modernize their application layer—moving to containers or microservices—only to find that a shared monolithic database continues to create dependencies that undermine agility. Based on experience gained through the AWS Migration Acceleration Program (MAP), database decomposition remains one of the most complex but also most valuable steps in modernization.
A structured approach to database modernization helps organizations overcome these challenges while minimizing risk and disruption.
Why Decompose Monolithic Databases?
When executed correctly, database decomposition delivers tangible business and technical benefits:
- Greater business agility. Teams can deploy and evolve individual services independently, significantly reducing time-to-market for new features.
- Optimized performance. Purpose-built AWS databases can be selected for specific workloads—for example, Amazon DynamoDB for low-latency transactional workloads or Amazon Redshift for advanced analytics.
- Improved cost efficiency. Independent scaling prevents over-provisioning and enables migration from expensive proprietary licenses to open-source alternatives such as Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition.
- Faster innovation. Teams are no longer constrained by a single database engine and can adopt the best database technology for each use case.
Assessing Your Database Landscape
Before starting decomposition, a detailed assessment is essential to build a solid business and technical foundation. This phase aligns closely with discovery and planning activities in AWS MAP.
Key assessment activities include:
- Analyzing schema complexity, stored procedures, triggers, and functions using AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT)
- Using AI-powered tools such as AWS Transform to generate modernization readiness reports
- Identifying dependencies and access patterns through automated discovery and database profiling tools
- Comparing current licensing and infrastructure costs with projected AWS costs, including license optimization opportunities
AWS also offers the Optimization and Licensing Assessment (OLA) to help organizations identify potential savings during migration planning.
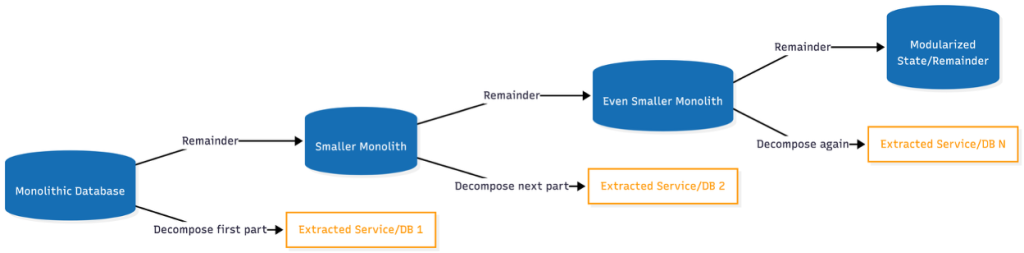
A Structured Framework for Database Decomposition
AWS best practices define a proven, four-stage framework for decomposing monolithic databases. This approach has been refined across numerous real-world customer engagements and helps reduce complexity while maintaining control.
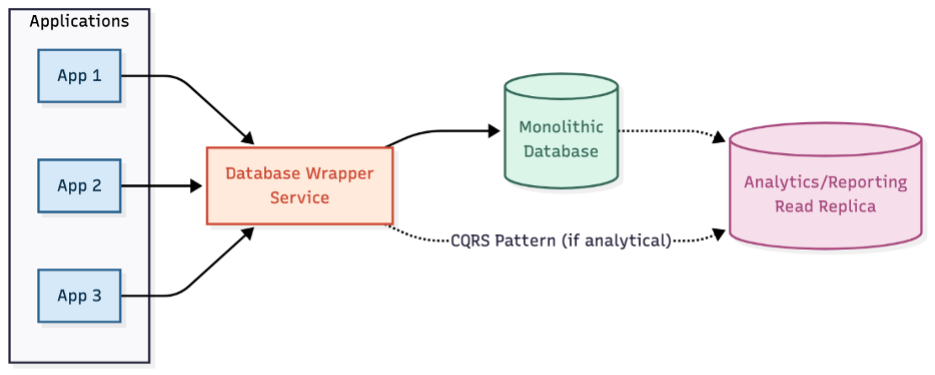
1. Controlling Database Access
The first step is to stop uncontrolled growth. This is achieved by introducing a database wrapper service that becomes the only authorized access point to the monolithic database.
This approach:
- Creates clear ownership and access boundaries
- Provides visibility into usage patterns
- Establishes a foundation for gradual decomposition
For analytics-heavy workloads, applying the CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) pattern allows read workloads to be isolated from transformation activities.
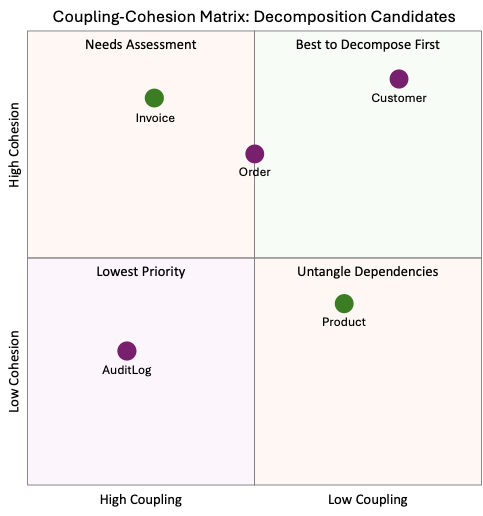
2. Analyzing Coupling and Cohesion
Identifying natural decomposition boundaries requires understanding how database components interact. Tables with high cohesion and low coupling are ideal starting points.
Tools such as SchemaSpy, CAST Imaging, and native database profiling utilities help visualize relationships and prioritize candidates. Early wins in this phase build confidence and momentum for further modernization.
3. Migrating Business Logic Out of the Database
True service autonomy requires moving business logic from stored procedures, triggers, and functions into the application layer.
AWS tools significantly accelerate this process:
- AWS SCT for schema and code analysis
- AWS Transform to automate stored procedure conversion and refactor dependent application code
- Amazon Q Developer to assist with application code modernization
These capabilities reduce manual effort while preserving logic and data integrity.
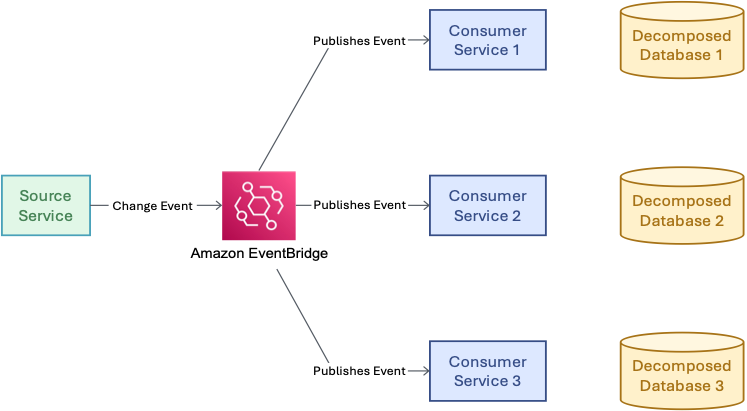
4. Decoupling Table Relationships
The final step focuses on removing tight dependencies created by joins and foreign keys. Proven strategies include:
- Denormalization to improve performance and service independence
- Reference-by-key to replace foreign keys with service-level identifiers
- Event-driven synchronization using Amazon EventBridge or Amazon SNS to propagate data changes asynchronously
These patterns enable independent evolution and scalable, resilient architectures.
Aligning with AWS Modernization Programs
Database decomposition fits naturally into broader AWS modernization initiatives. Organizations often follow a phased journey: migrate to AWS, modernize applications, decompose databases, and adopt cloud-native patterns.
This approach aligns closely with the AWS Well-Architected Framework, particularly:
- Operational Excellence – independent deployments and faster recovery
- Performance Efficiency – purpose-built databases
- Cost Optimization – granular scaling and license reduction
Programs such as MAP and Modernization Experience-Based Acceleration (ModAx) provide technical guidance and potential funding to support these transformations.
Measurable Cost and Operational Benefits
Database modernization on AWS delivers quantifiable improvements:
- License cost reduction of up to 60–90% by moving to open-source engines
- Right-sized infrastructure aligned to real workload demand
- Lower operational overhead through managed services such as Amazon RDS and DynamoDB
- Improved resource utilization through independent scaling
AWS Services That Accelerate Database Modernization
Key AWS services supporting database decomposition include:
- AWS Transform for SQL Server – AI-powered, full-stack modernization and code refactoring
- AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) – low-downtime migration with change data capture
- AWS Schema Conversion Tool (AWS SCT) – automated schema conversion and assessment
Together, these tools significantly reduce modernization timelines and risk.
Getting Started with Softprom and AWS
Organizations beginning their database modernization journey should:
- Assess and prioritize decomposition candidates
- Engage AWS expertise and MAP support
- Establish governance for security, data consistency, and compliance
- Build internal skills using AWS training resources
As an official AWS Partner, Softprom supports customers at every stage—from assessment and architecture design to migration, modernization, and ongoing optimization.
Conclusion
Database decomposition is a critical step toward unlocking the full value of cloud-native architectures on AWS. A structured, phased approach—combined with modern AWS tooling and AI-powered automation—makes this transformation faster, safer, and more accessible than ever before. With deep experience in AWS modernization programs, Softprom helps organizations reduce risk, optimize costs, and achieve true business agility by transforming monolithic databases into scalable, future-ready architectures.







