Fake e-mail bill from the tax office - how many victims will there be?
News | 18.11.2021
DISCLAIMER: This article is not a call to action, it is written for educational purposes to draw attention to an issue.
What do you think - is such a situation possible in principle??
Agree, it would be convenient if the tax authorities made a revolution and implemented the payment of the annual property tax for individuals through online payment in 3 clicks, and also provided a 60% discount to all those who paid online.
Is this possible - of course, it is possible, an e-mail from the tax office came to the mail, with the text according to which you were among the people for the focus group and if you pay the tax within 2 days, you will get a solid discount. There is no reason not to trust the letter from the tax office.
How events developed further: 4 days later, news feeds began to actively publish news about mass spoofing on behalf of the tax authorities and about thousands of victims of the actions of fraudsters who sent messages on behalf of the tax office.
Is such a situation possible in principle - of course not, you will say, because the tax inspectorate would never allow such a situation, and fraudsters will not mask under public service, because this will cause a large-scale resonance.
But is it? We decided to check and make sure that it is impossible to carry out the above actions. To do this, we analyzed the domain names of tax authorities in 4 easten europe countries for vulnerabilities by 3 markers:
We checked the correctness of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC settings.
1.What is SPF?
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a record that provides an understanding between the sender's and recipient's mail servers. It contains information about from which IP addresses mail from your domain can be sent.
One SPF record corresponds to one domain.
For example, the recipient server requests SPF during message delivery. If the sender has this record, he passes in it a list of IP addresses from which he can send mail. As a rule, this is data from one or several mail servers.
The recipient server checks the IP address of the sender's mail server against the list from the SPF. If he finds the required IP in the list, he skips the message further.
This is the first marker that indicates that it is you who are sending information on behalf of your domain.
Therefore, setting SPF is important for secure communication and increasing the delivery rate of your mail. And as practice shows, the SPF record is configured correctly for most senders.
2.What is DKIM?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is the second stage of protection when transferring data between mail servers. It is a mechanism that works through encryption keys. In order to activate it, you need to create two keys: private and public.
Private is your personal unique key that encrypts a hidden signature in the headers of each of your letters. He is not visible to users.
You enter the public key into your DNS records, it is a signature in txt format.
An example of a public key:

The two keys work in tandem. When the recipient's server sees an email, it asks for your public key. With its help, he decrypts the hidden signature, which confirms your authorship.
Accordingly, if you do not have DKIM installed, many mail servers will reject receiving your letters. This is an authorization method that cannot be ignored.
3.What is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is the third stage of protection. It is a technology that determines what to do with your messages if they are not authenticated with SPF and DKIM. This is the rule you set for emails sent on your behalf.
So, you protect your recipients from abuse of your reputation, use of your domain by scammers.
Before installing DMARC, it is important to make sure that SPF and DKIM are specified correctly, otherwise this may lead to filtering letters from you.
4.How the mail protection mechanism and protection against spoofing works.
There are three basic rules by which the DMARC mechanism works when it recognizes messages as suspicious:
- Takes no action;
- Marks email as spam and quarantines;
- Rejects the message without delivery to the addressee.
The results with the current security settings of the postal services of the tax services of the 4 Eastern European countries are shown in the table below:
* we have closed the "*****" country of the tax authority, in which has identified security problems in the settings of postal services.
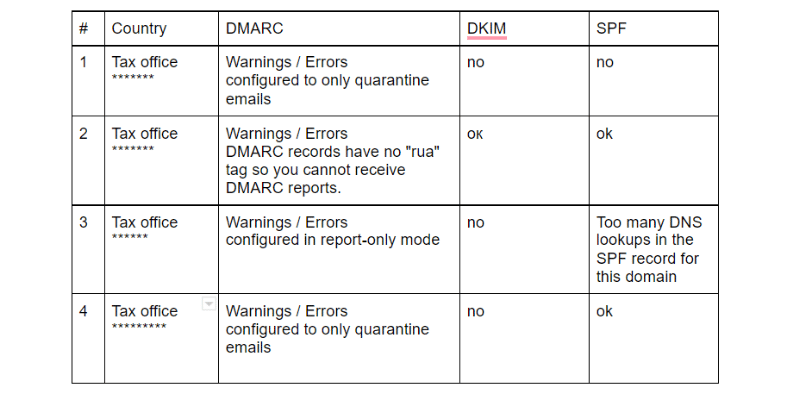
Conclusions: spoofing mailing from all tax services of 4 countries is possible. The result is extremely unsatisfactory.
There are many instructions on the network with the detailed configuration of each of the protocols, but the procedure is quite laborious and requires some knowledge. You can also use the solution from the Red Sift company, which will provide a detailed checklist for setting up.
If you need advice, project calculation, or a test version of the solution, you can leave an application through the form:
FAQ on the main mechanisms for protecting your mailings:
DNS-server - stores information about the domain and its IP addresses. You can add SPF and DKIM (public key) records to DNS through your domain name registrar.
SPF – a record containing information about the mail servers from which you send messages. If you receive letters from IP other than those specified in the SPF, they will not be authenticated.
DKIM – encryption-based protection mechanism. The public key is entered into DNS records and is readable, while the private key encrypts your hidden signature in message headers. Decryption occurs when messages are delivered by the recipient.
DMARC – a set of rules for letters on your behalf that did not pass SPF and DKIM authentication.







